The Hope spacecraft orbiting Mars has revealed astonishing details about the moon Deimos. The UAE mission’s most recent observations of the moon challenge the long-held belief that Deimos is an asteroid captured by Mars’s gravity and compelled to orbit it.
Deimos and Phobos are two moons of Mars. Deimos orbits Mars every 30 hours, while Phobos orbits every 30 hours. The Hope mission crew presented their most recent findings at the General Assembly of the European Geosciences Union.
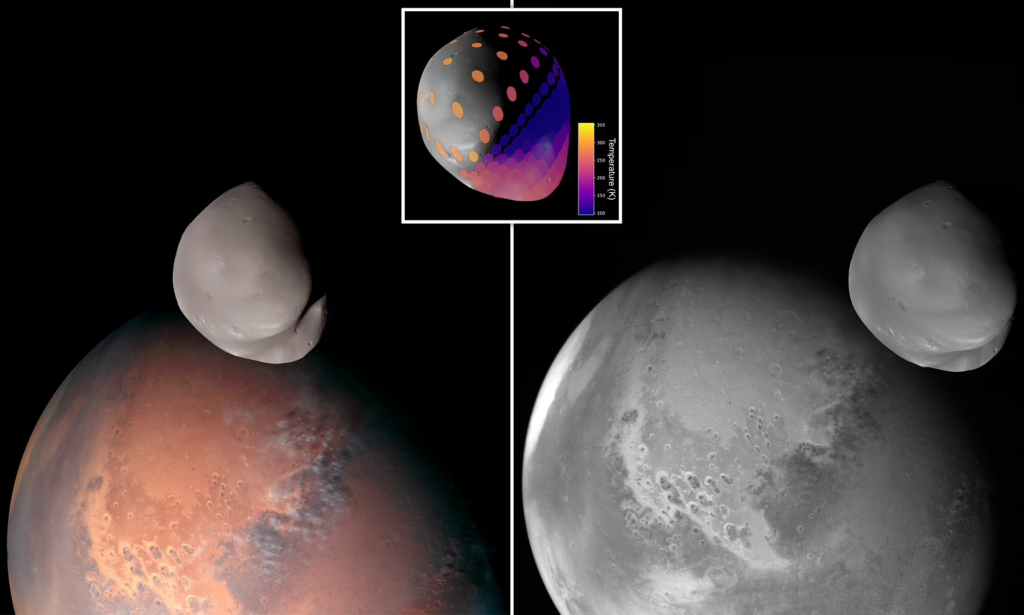
The UAE’s Minister of State for Public Education and Advanced Technology, Sarah Al Amiri, announced that the Hope Mars Mission science team has made a series of groundbreaking observations of Mars’ smaller moon, Deimos, utilizing all three of its scientific instruments.
Deimos and Phobos orbit Mars. Deimos orbits Mars every 30 hours, but Phobos is larger.
The Hope probe’s mission around Mars has been extended for an additional year. “Given the remarkable performance of the Hope Mars Mission, which exceeded all expectations, and the great achievements of the EMM’s science team in providing new findings about Mars to the global scientific community, we are extending the Emirates Mars Mission for an additional year,” tweeted Sarah Al Amiri.
As part of its observation of Deimos, the Hope spacecraft conducted close flybys that brought it to within 100 kilometers of the asteroid. Long believed to be a captured asteroid, the Moon may have a planetary origin, as suggested by the observations. In addition to taking photographs, the spacecraft conducted ultraviolet and infrared observations, amassing data on previously unexplored regions of Deimos.
Hessa Al Matroushi, the EMM’s science lead, said in a statement, “One long-standing theory is that they are captured asteroids, but there are still questions about their composition.”
According to Al-Matroushi and other scientists from the UAE Space Agency, these new images indicate that Deimos is not an asteroid that was captured in Mars’ orbit eons ago. Instead, they assert that the moon is likely of Martian origin, possibly originating from the larger Martian moon or Mars itself.

The Hope probe will continue its mission for another year.
The spacecraft, also known as the Amal probe, arrived in orbit around Mars in February 2021 and has since made significant observations, such as observing the elusive discrete auroras on Mars’ nightside and capturing never-before-seen images of Martian dust storms.
According to al-Matroushi, Amal will continue to surpass Deimos this year, but not as closely as on March 10.
The spacecraft captured the expansive dust storm pounding the planet’s surface as it grew to a width of over a thousand kilometers. In addition to observing the dust storm, the probe captured an image of Mars that was totally illuminated and nearly centered on Syrtis Major. Furthermore, it reveals the increasing density of this diffuse dust atmosphere.
“We are very proud of our talented scientists. We are proud of our scientific achievements. “Proud of our contribution to the advancement of human knowledge,” tweeted the UAE’s prime minister, Sheikh Mohammed bin Rashid Al Maktoum.

